Transients
Transient decomposition using a de-clicking algorithm
Transients implements a “de-clicking” algorithm based on the assumption that a “transient” is an audio sample or series of samples that are anomalous when compared to surrounding audio samples. It creates a model of the time series of samples, so that when a given sample doesn’t fit the model (its “error”, or “anomalous-ness”, goes above the threshold argument threshFwd) it is determined to be a transient. The series of samples determined to be a transient will continue until the error goes below the argument threshBack, indicating that the samples are again more in-line with the model.
After identifying transients, the algorithm then estimates what “should have happened” during the transient period if the signal had followed its non-anomalous path, and resynthesises this estimate to create the residual output. The transient output is input signal - residual signal, such that the summed output of the object (transients + residual) will null-sum with the input.
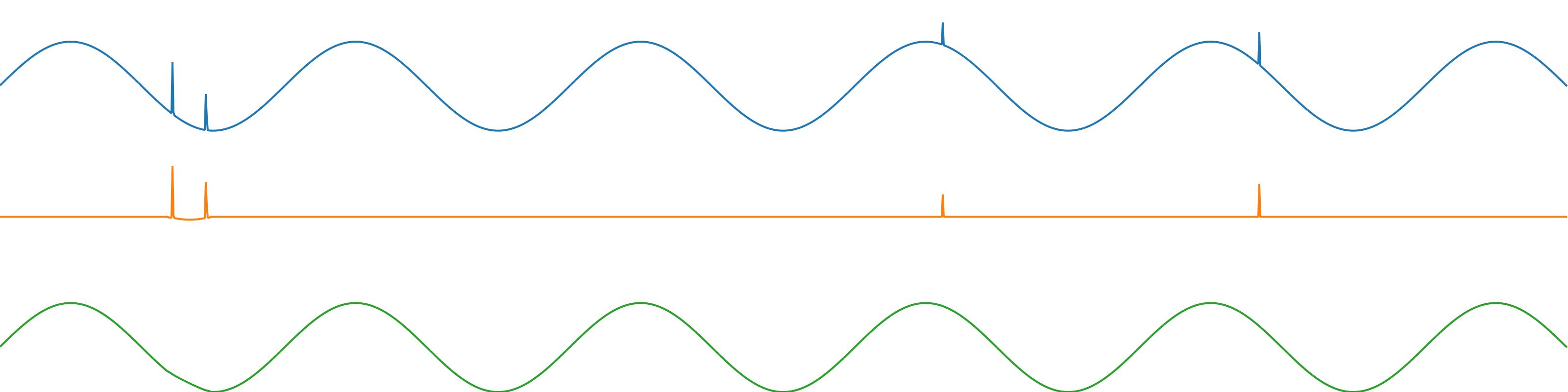
An original signal (blue), the residual (green) signal with the transients removed, and the transients (orange).
Audio Example
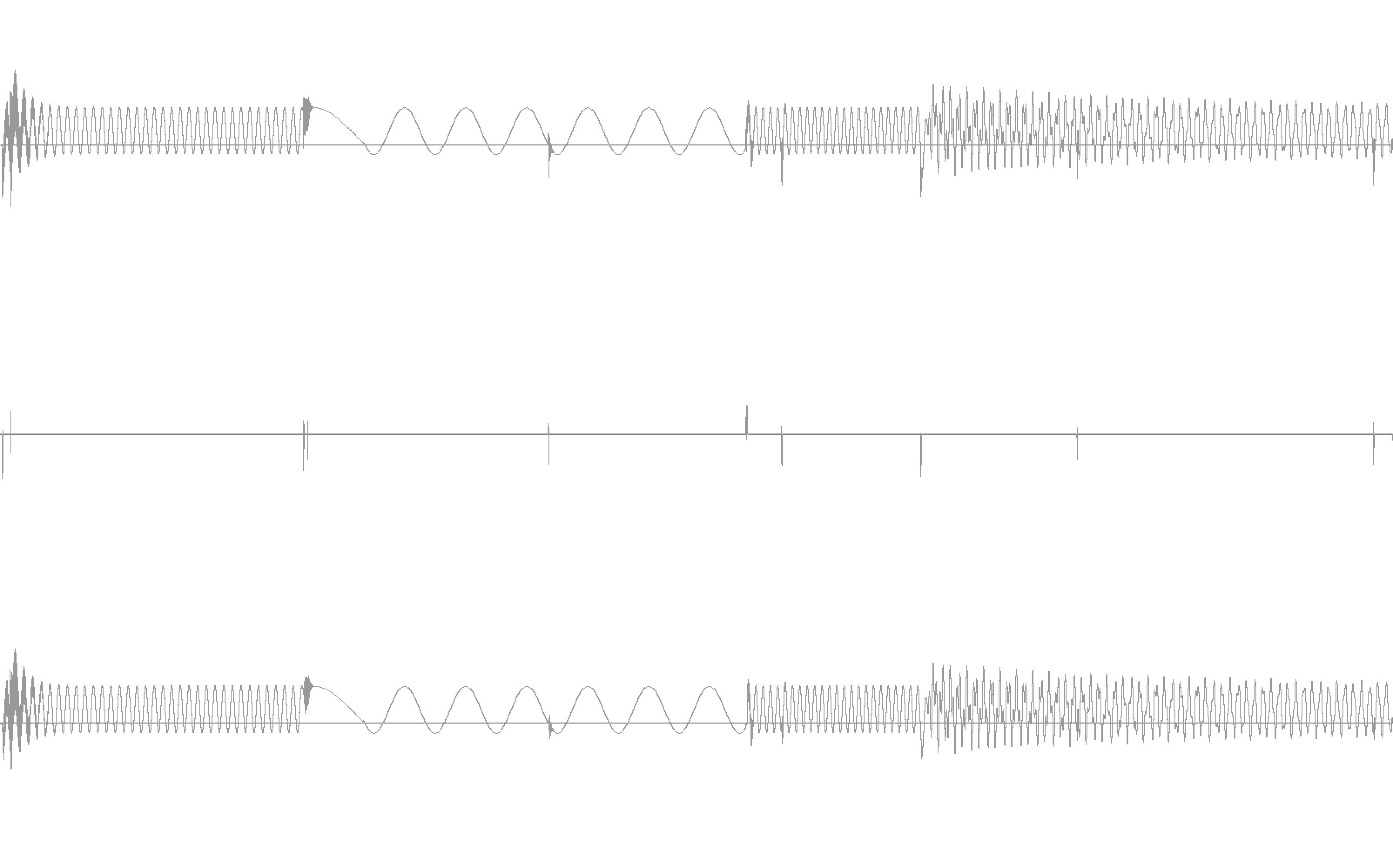
An original signal (top), the residual (bottom) signal with the transients removed, and the transients (middle).
